Deployments
Learn how Globe creates versioned builds of your app, manage preview and production deployments, and track your application across environments.
A deployment is a versioned build of your application that runs on Globe's global edge network. When you run globe deploy or push to GitHub, Globe creates a new deployment with a unique URL and a human-readable name (e.g., calm-river, bright-mountain). Use deployments to preview changes, push live updates, and track your application across different environments.
Preview Deployments
Preview deployments let you test, review, and share work in progress without affecting your live application. They're ideal for internal review, staging, or QA before releasing to users.
Preview deployments:
- Won't affect your live production app
- Use temporary URLs (e.g.,
abc123xyz.globeapp.dev) - Are perfect for testing changes before going live
Create a preview deployment by:
- Running
globe deployin your terminal (without the--prodflag) - Pushing to any branch that is not set as your production branch in project settings
Production Deployments
Production deployments serve the live version of your application to end users. Trigger one when you're ready to release updates. Each new production deployment replaces the previous one.
Production deployments:
- Replace the current live version of your app
- Persist until replaced by a new production deployment
- Use your custom domain (if connected), or a default URL like
your-project.globeapp.dev
Create a production deployment by:
- Running
globe deploy --prodin your terminal - Pushing to the branch marked as your production branch (default:
main) when GitHub integration is enabled
Deployment Names
Each deployment receives a human-readable name (e.g., calm-river, bright-mountain) instead of random character strings. These friendly names make it easier to identify, reference, and discuss specific deployments in your team. Deployment names are automatically generated and appear in the dashboard and CLI output for both preview and production deployments.
How to Manage Deployments
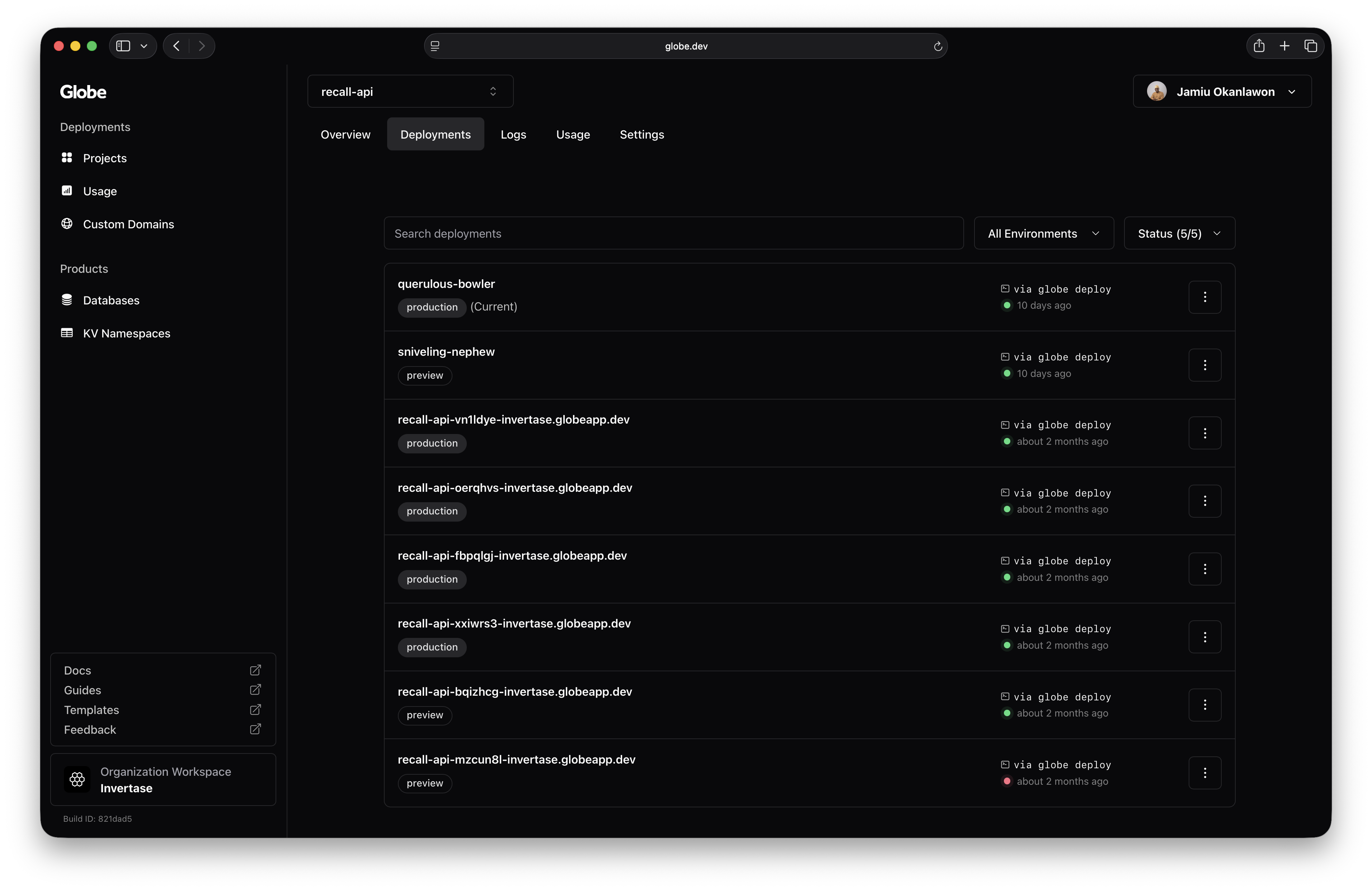
You can view and manage all your deployments in the Globe dashboard:
- In the Globe dashboard, go to your project
- Open the Deployments tab
- Toggle between Preview and Production to filter deployments by type
- Toggle between statuses (Queued, In Progress, Deployed, Failed, Cancelled) to filter deployments by status
- Select any deployment to view:
- Deployment status and timing
- Commit information (for GitHub deployments)
- Direct URL to access the deployment
- Build logs and runtime logs
- Click the deployment URL to open it in your browser
How Deployments Work
Every deployment goes through five stages from start to finish:
- Source Acquisition: Globe fetches your code from your local machine (CLI) or GitHub repository (GitHub integration)
- Build Process: Your code is compiled and built according to your project's configuration, including framework presets, build commands, and dependencies
- Containerization: The build output is packaged into a container optimized for Globe's infrastructure
- Distribution: The container is distributed to Globe's global edge network across multiple regions
- Activation: The deployment becomes accessible via a unique URL and is ready to serve traffic
Deployment times vary based on your project size and complexity. Most
deployments complete in 1-3 minutes. You can monitor progress in the dashboard
or via CLI with the --logs flag.
Deployment Status Reference
| Status | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Queued | Deployment is waiting to be processed |
| In Progress | Globe is building your application |
| Deployed | Successfully deployed and available through its URL |
| Failed | Build or deploy process failed |
| Cancelled | Deployments were manually stopped before completion |
Best Practices
- Use preview deployments to test every major change before deploying to production
- Enable branch protection in GitHub to prevent accidental production deploys
- Use different environment variables for preview and production deployments
- Check logs on failed deployments for quick debugging and troubleshooting
- Always verify preview deployments work correctly before promoting to production
Related Topics
- Logs - Monitor build outputs, runtime errors, and real-time activity
- Build Settings - Configure how your app is built and deployed
- Environment Variables - Set environment-specific values for deployments
- Domains - Configure custom domains for your deployments
- GitHub Integration - Automate deployments from GitHub
