Environment Variables
Environment variables are a set of named values that can affect the way running processes will behave on a deployment. An environment variable can be used to store secret values that are not safe to be stored in the codebase. You may wish to use different values for different environments, such as preview, and production to connect to different databases or API endpoints.
Creating environment variables
To create a new environment variable, navigate to the Environment Variables tab in the Settings section of the project on the dashboard. Click the Add Variable button.
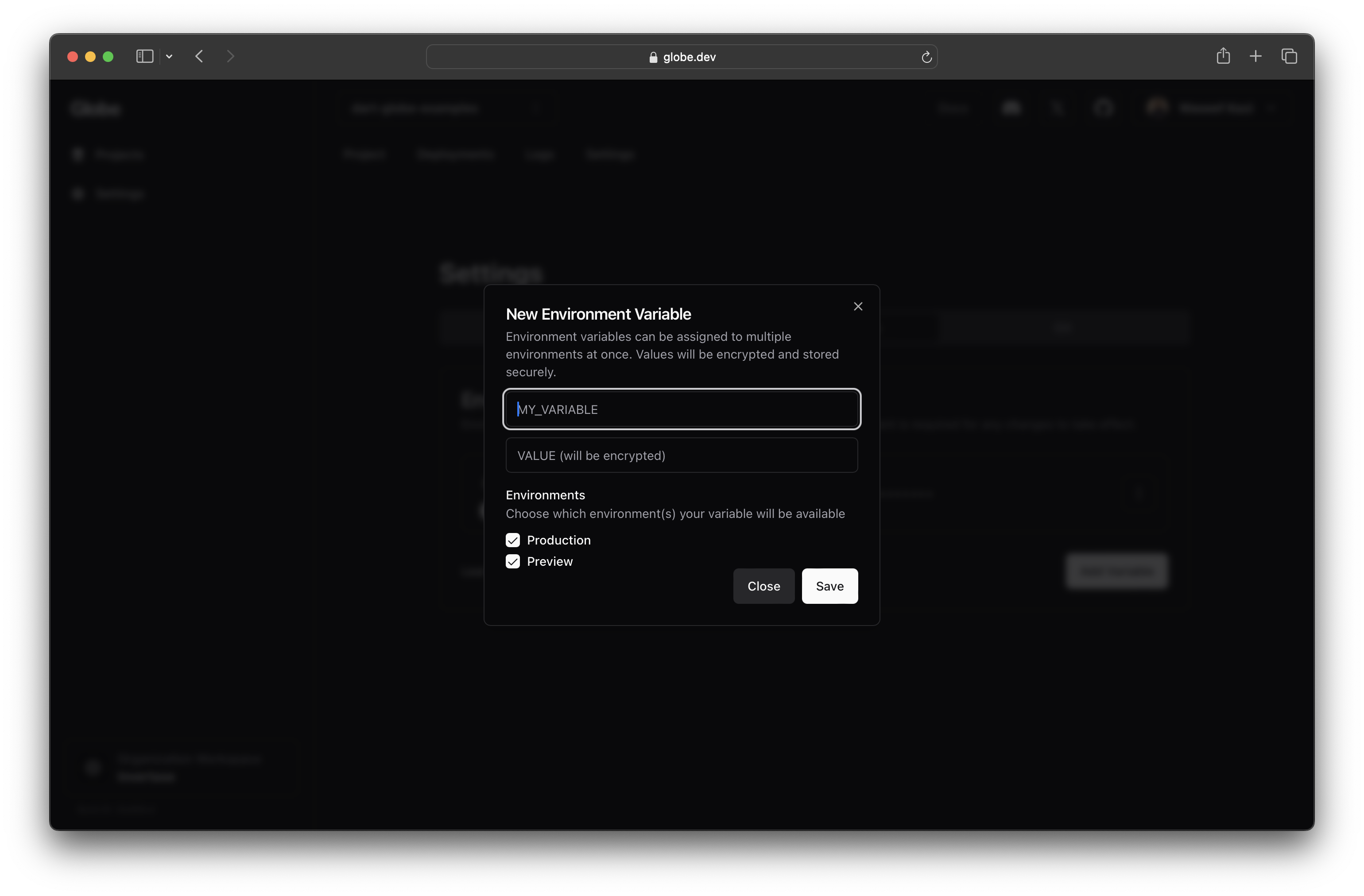
Enter the name and value of your variable. All values are encrypted, and can only be viewed by specifically viewing it on the dashboard.
It is also possible to specify what environments the variable should be available in.
After creating or deleting an environment variable, you will need to redeploy your project for the changes to take effect.
Accessing environment variables
Within your Dart code, you can access environment variables using the Platform.environment map. Any package that uses this map can access Globe environment variables as well.
String? value = Platform.environment['MY_VARIABLE'];
Using "dotenv" package
If you prefer to use a .env file for local development, you can use the dotenv package to load values from the .env file locally and use environment variables when deployed.
When your app is deployed to Globe, any static assets are ignored, so you need to pass includePlatformEnvironment: true to the DotEnv constructor to include platform environment variables that you previously defined on Globe dashboard (Project > Settings > Environment variables).
final env = DotEnv(includePlatformEnvironment: true)..load();
String? value = env['MY_VARIABLE'];
System environment variables
Your deployed Dart application has access to the Globe-specific environment variables which wouldn't be typically available while you develop/test your app locally. These are available on all deployments:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
PORT | The port that the application should listen on. |
GLOBE | Variable for checking if running in Globe. Will be set to '1' |
HOSTNAME | The hostname of your deployed application in Globe. |
CRON_NAME | Name of the cron job provided in the globe.yaml file. |
CRON_SCHEDULE | The cron schedule code. For example, * * * * * |
CRON_ID | Unique identifier for the defined cron job. |
CRON_EVENT_ID | Unique identifier for the current running cron job. |
- Cron environment variables are only available when a cron job is running.
